HOME
BRIEF INTRODUCTION
Dr. Pengyu Zhu is a Professor in the Division of Public Policy at Hong Kong University of Science and technology (HKUST). He is also the Director of the Center for Applied Economic Social and Environmental Research, Associate Director of GREAT Smart Cities Institute.
He has taught courses on transportation and land use, transportation economics, economics applications to planning and policy, urban economics, urban geography, quantitative research methods, and urban design and site planning studios.
To date, his work has been published in major academic journals such as Landscape and Urban Planning, Urban Studies, Annals of Regional Sciences, Transportation, Transportation Research Part A/D, Urban Geography, Cities, Regional Science and Urban Economics, and International Journal of Environmental Science and Technology. He was also among the world’s top 2% scientists in 2023 and top 1% in 2024, based on TopResearchersList.com ranking by Elsevier and Stanford University. In recognition of his outstanding achievements and academic excellence, Prof. Zhu has been recently awarded 5.2 million HKD and conferred the esteemed title of ‘RGC Research Fellow‘, a prestigious recognition from the Hong Kong Research Grants Council (RGC) under their Research Fellow Scheme (RFS) in support of only the most outstanding scholars in Hong Kong. Notably, Prof. Zhu was the only awardee under the Humanities, Social Sciences, Economics and Business Studies Panel (H-Panel) in 2024, while the other awardees were recognized under the Sciences, Medicine, Engineering and Technology Panel (S-Panel).(MORE ON BIOGRAPHY)
Research Highlights
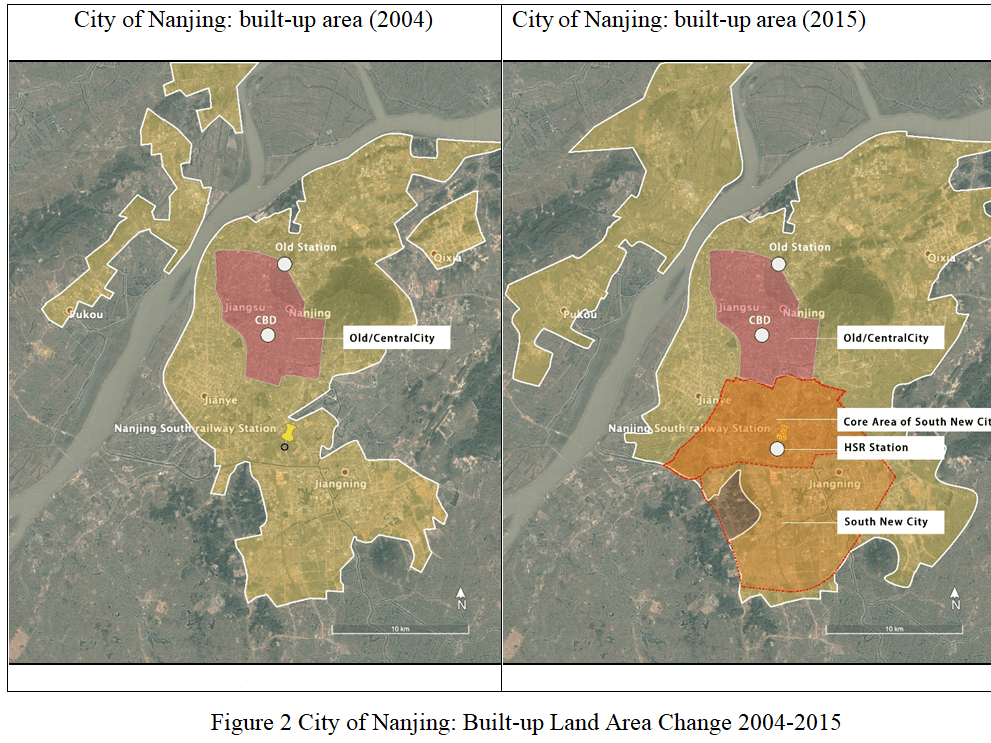
Results: Being connected to the HSR network on average leads to a 11.2% faster rate of growth of urban built-up areas. Causes and mechanism for such heterogeneity are also elaborated, together with the policy and planning implications.
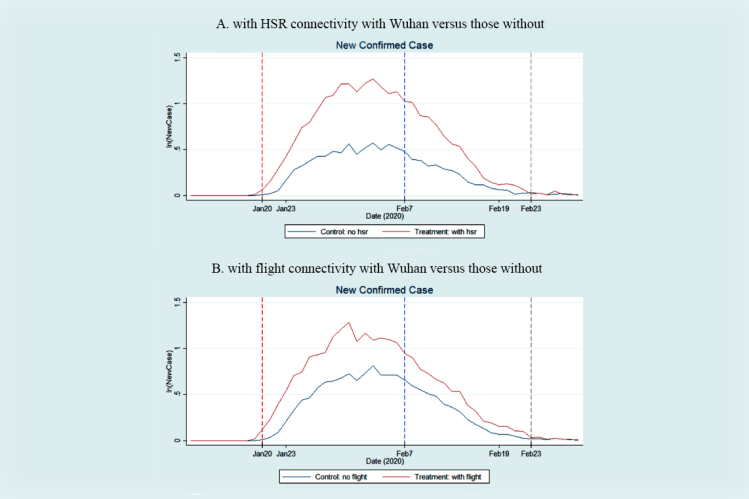
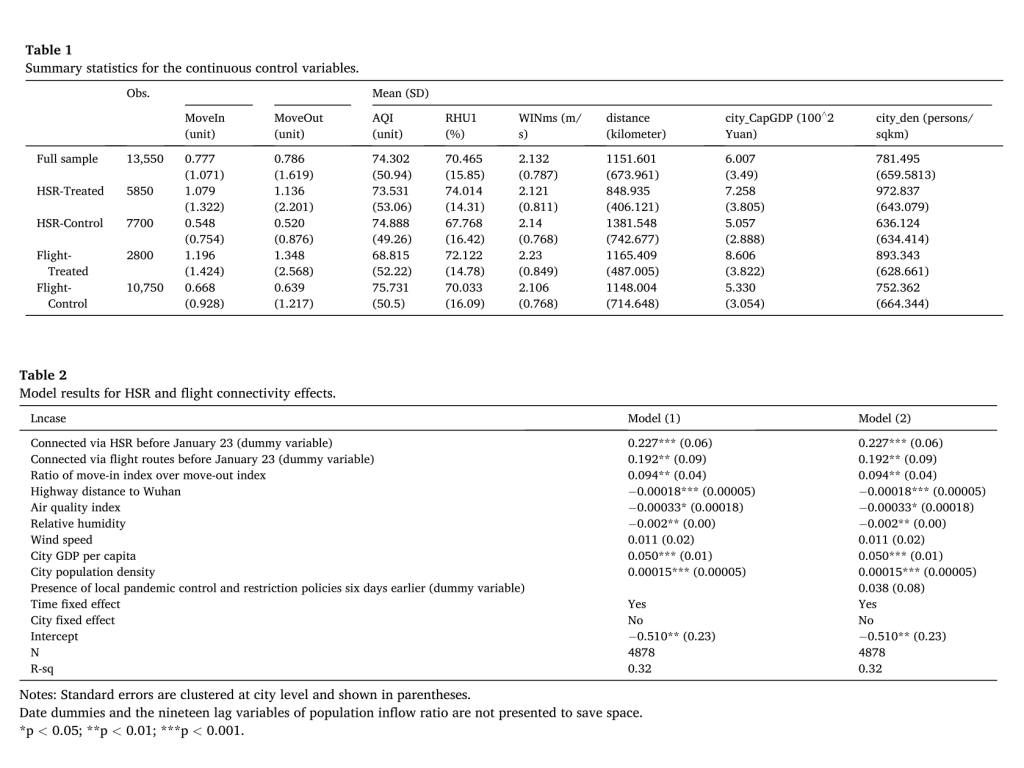
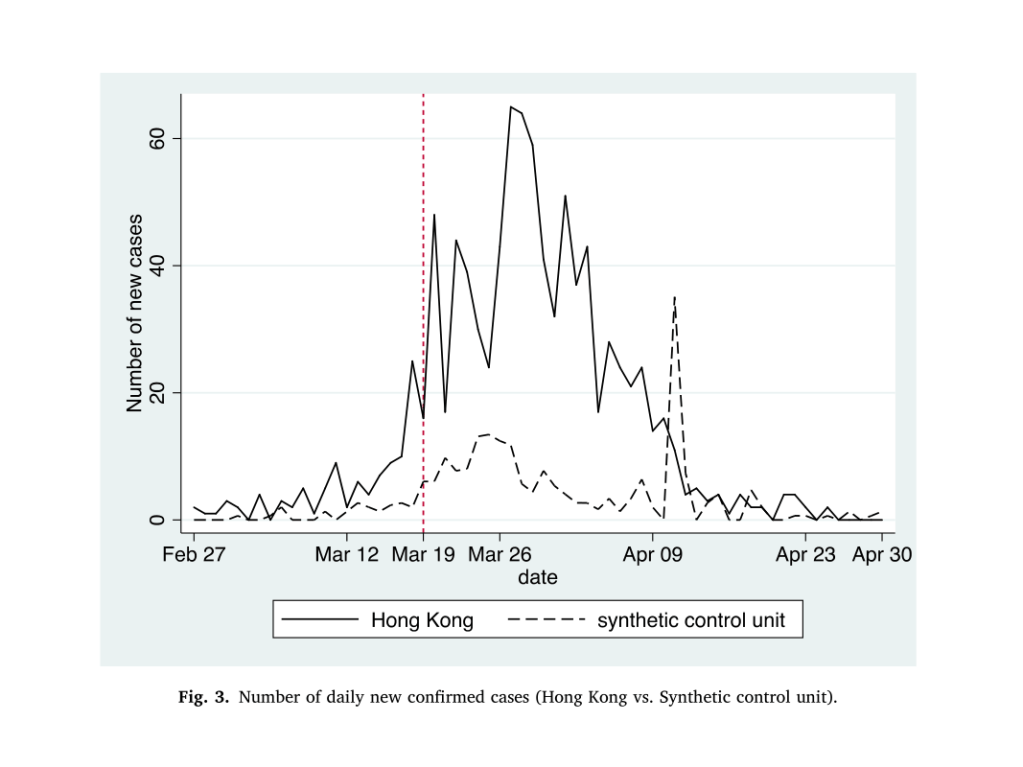
Results: We find high-speed rail (HSR) and air connectivity with Wuhan resulted in 25.4% and 21.2% increases in the average number of daily new confirmed cases, respectively, while their suspension led to 18.6% and 13.3% decreases in that number.
Results: The ifection rate under home quanrantine later converges with the counterfactual estimate under centralized quanrantine (0.136% vs. 0.174), suggesting similar efficacy in the later face of implementation. Accordingly, compulsory home quanrantine is feasible.
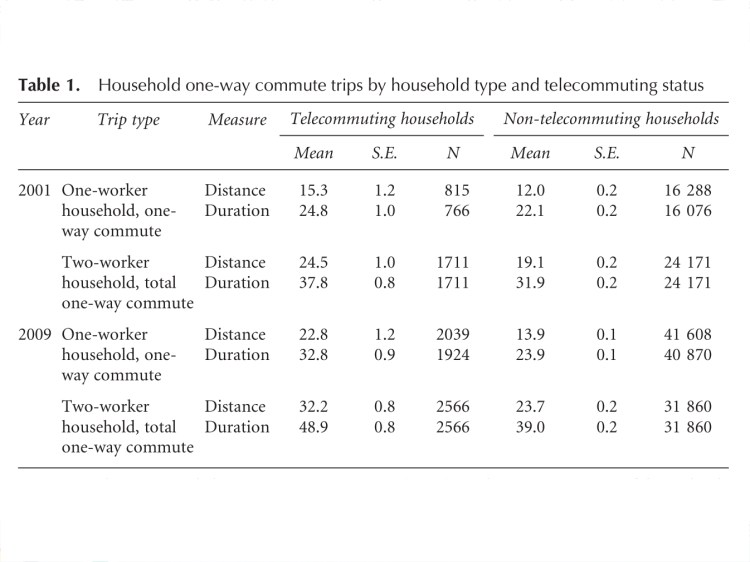
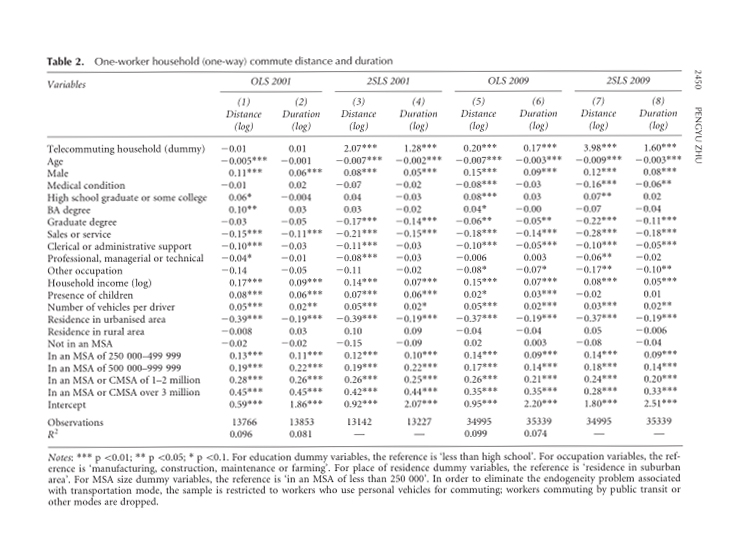
Results: These findings suggest that telecommuting (two-worker) households tend to choose locations involving a longer total one-way commute than non-telecommuting households, and this difference is largely due to the longer commute of their telecommuting members.
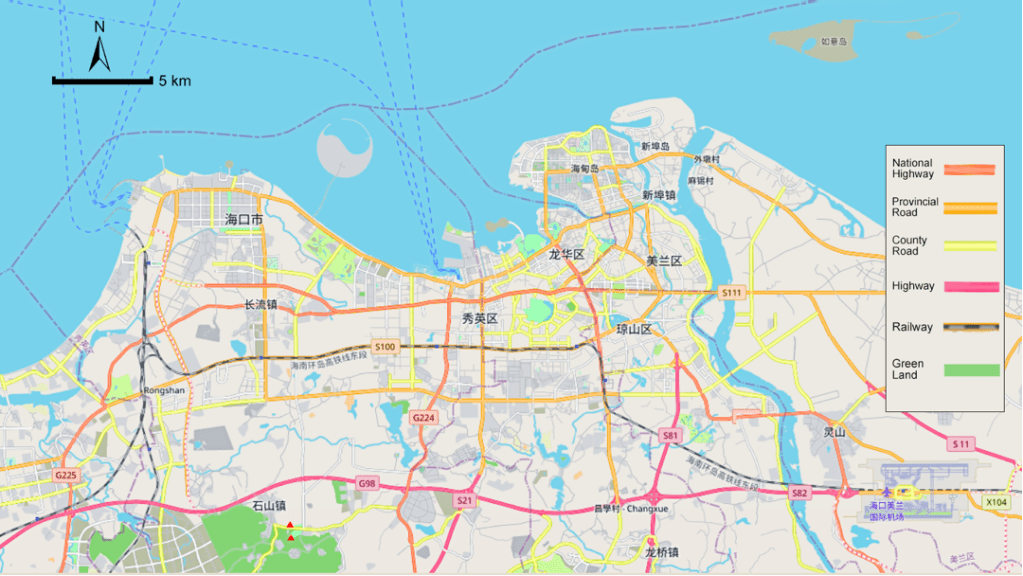
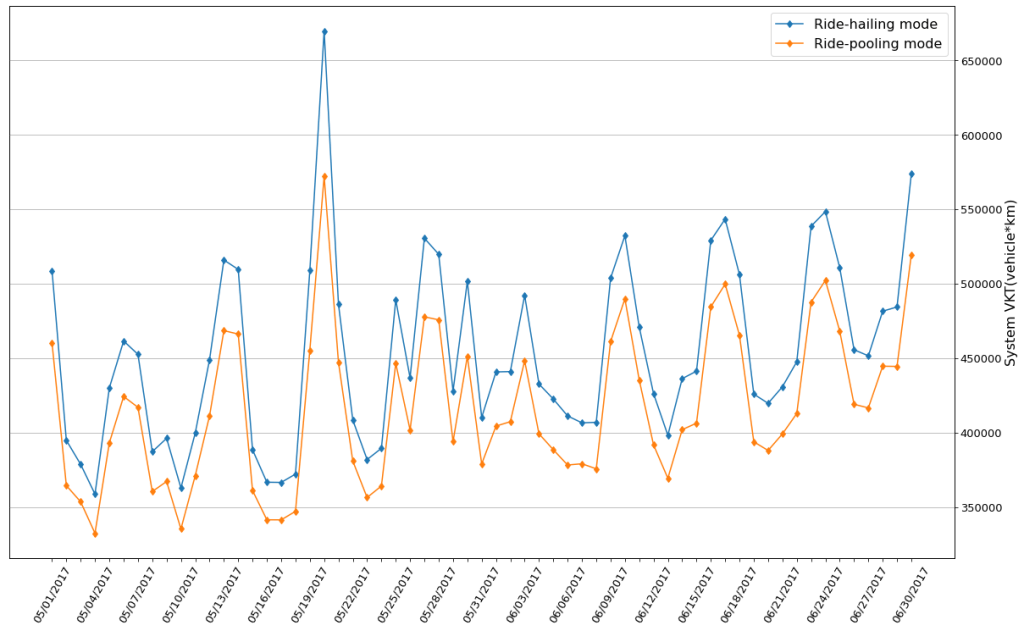
Results: We find that under our initial assumptions, with a buffer time of 60s, ride-pooling has the potential to reduce aggregate VKT by 8.21% as compared to standard ride-hailing mode in a mid-sized city, Haikou. This reduction in VKT is equivalent to a savings of 1,234,164 Liters in petroleum consumption and 3308 tons in carbon emissions annually.
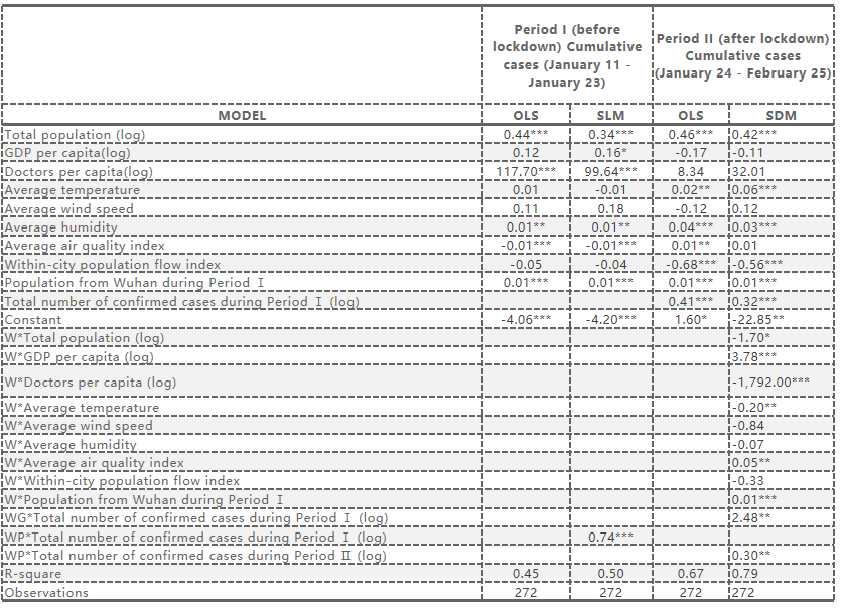
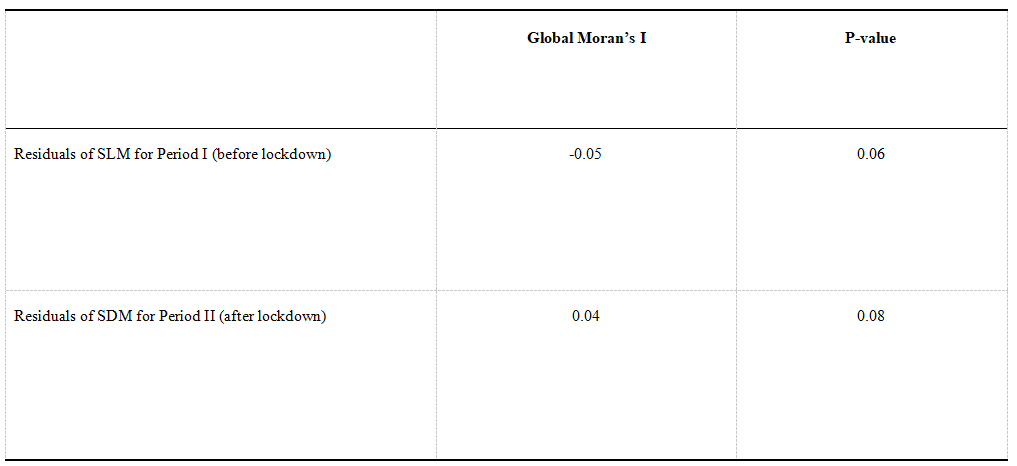
Results: We further compare the performance of the spatial econometric models using different SWMs for each period. Regardless of whether the population-flow-based SWM or inverse distance SWM was used, the global Moran’s I tests for Period I consistently exhibit significantly positive values, confirming the existence of spatial autocorrelation in the dependent variable. However, as mentioned in section 4.3, LM tests and robust LM tests indicate that spatial models (e.g., SLM, SEM) based on inverse distance SWM fail to capture such spatial autocorrelation in the dependent variable and these models perform no better than the OLS model. On the other hand, spatial models using population-flow-based SWM for the spatial lagged dependent variable successfully address the spatial autocorrelation issue, with the model residuals exhibiting no systematic spatial pattern at a 95 percent confidence level.